Why the RAN Intelligent Controller is the Brain of Open RAN Networks
Introduction
RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) represents the next evolution of mobile networks’ RAN controller and management systems and is a major step toward the vision for self-optimizing networks.
Network Complexity Intensifies
Mobile network operators are facing strong pressures to evolve their businesses and operations to support profitable growth. Explosive demand for mobile bandwidth persists, while ARPUs have been flat and declining. On top of that, mobile telecommunications networks becoming more complex. Supporting multiple access networks for 2G, 3G, 4G and now 5G, requires ever more RAN capacity and denser networks. 4G networks are roughly 10x denser than 3G networks, and further network densification will be a critical part of deploying 5G architecture, especially to achieve the promised increased data rates and ultra-reliable lower latency.

Bringing SDN to the RAN
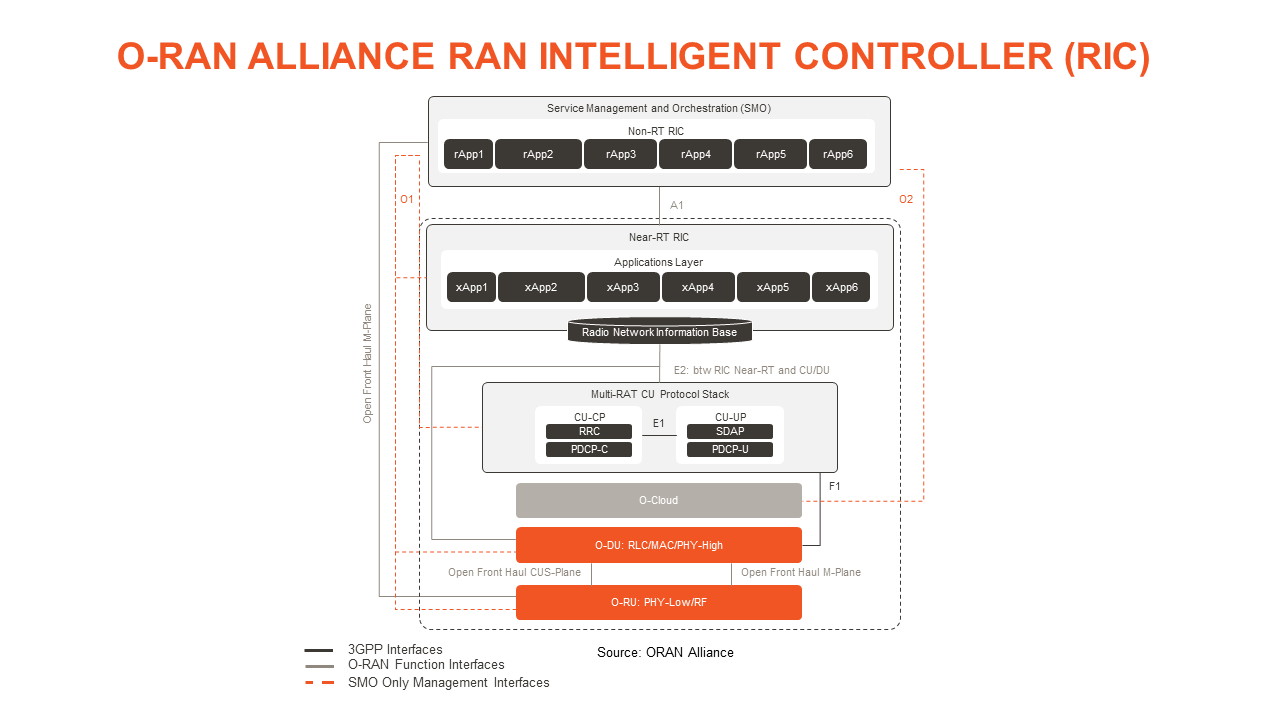
Open RAN disrupts traditional closed and proprietary RAN solutions by offering true hardware and software disaggregation which helps operators reduce deployment cost and complexity. The Software Defined Networking (SDN) approach that Open RAN brings to communications networks centralizes network intelligence in a network element by disassociating the forwarding process of network packets (data plane) from the routing process (control plane). This allows operators to independently scale control plane and data plane as required. The control plane consists of one or more controllers, which are considered the brain of an SDN network. In the O-RAN Alliance’s Open RAN architecture, the mobile base station has been split between the Distributed Unit (DU) and the Central Unit (CU). Furthermore, the CU has been split into the central unit – control plane (CU-CP) and the central unit – user plane (CU-UP). The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) further separates the control plane of the network from the RAN CU and DU nodes, allowing operators to bring software-defined controllability to the RAN to increase system performance.
RIC is Wicked Smart!
The RIC is divided into non-real-time and near-real-time components. The Non-RT RIC is an element of the operator’s centralized Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) Framework, as defined by the O-RAN Alliance. Using specialized applications called rApps, the Non-RT RIC enables “greater than 1-second control” of RAN elements and their resources. It also provides network data, performance metrics, subscriber data, and AI-based recommendations for network optimization and policy guidance to xApps running on the Near-RT RIC, which in turn provides policy feedback to the Non-RT RIC. The Near-RT RIC resides within a telco edge or regional cloud and typically enables network optimization actions that take between 10 milliseconds to one second to complete. The RIC rApps and xApps provide RAN programmability and flexibility, while making use of concepts like AI/ML, policy guidance, and enrichment info-based analytics to execute and realize the business needs of the operator. These applications can be built by the RAN vendor, the operator and/or third parties. The diagram below illustrates these Open RAN and RIC elements. For a more in-depth discussion of the RIC, see our Parallel Wireless overview: Role of the RAN Intelligent Controller.
The Apps are Where It’s At
The O-RAN Alliance has defined many use cases that RIC xApps and rApps can support, and which will enable MNOs to provide use case-driven, automated, and fine-grained control and management of the RAN resources. These use cases will help operators enhance user experiences with improved coverage and capacity, as well launch new revenue-generating services. Some examples of RIC-enabled use cases include Traffic Steering, which intelligently and proactively manages traffic load for improved user experiences and RAN Slice SLA assurance which is an important capability for emerging 5G enterprise applications requiring services from the network such as enhanced end to end security or low latency performance. We’ll see other “phase 1” use cases focused on the highest priority needs of most operators. Later “phase 2” uses cases will deal with specialized vertical applications, like UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) and V2X (Vehicular to Anything) use cases that require specific network requirements. At MWC Barcelona 2022, Parallel Wireless and Juniper Networks made an announcement with Open RAN early adopter Turk Telekom to trial Juniper Networks’ RIC framework and Parallel Wireless’ Open RAN solutions in testing 2 RIC use cases: Admission Control and Traffic Steering.
Is RIC the New SON?
SON, of course, means Self Organizing Networks. Some view RIC as the next generation of SON for Open RAN. The RIC solution can either augment traditional SON or repackage SON use cases to provide a flexible, standards based, interoperable, multivendor, programmable solution for RAN optimization. RIC will be critical for mobile operators to efficiently manage the complexity and costs of their expanding networks.
Want More?
Parallel Wireless is the industry leader in Open RAN. We believe Open RAN opens up possibilities and enables people around the world to be connected whenever, wherever, and however they choose. To learn more about our RIC solutions, watch our recent webinar on the RAN Intelligent Controller here.