The Future of Open RAN: 7 Predictions for 2022
Open Radio Access Networks (RAN) has been gaining momentum over the past few years and will continue to do so in 2022 and beyond. According to Dell’Oro Group, cumulative Open RAN revenue from 2020 to 2025 could be as high as $15 billion, with Open RAN revenues accounting for more than 10% of the overall RAN market by 2025. 5G technology adoption and enabling network deployments and upgrades at lower costs are driving more and more operators to choose an Open RAN approach for their network architecture.

As we look at the continued growth of Open RAN, our seven predictions for 2022 include:
1) Radio Ecosystem Will Continue to Expand
As Open RAN deployments take off, the ecosystem of radio providers is set to expand. Open RAN drives greater vendor diversity and supply chain security. Consolidation over the years has concentrated the RAN vendor market to a few major incumbent players. In fact, according to Deloitte, they still control 80% of the market. This is driving the urgency for an open approach. Operators across the globe need and want a wider ecosystem of telecommunication providers to increase cost competitiveness and drive innovation. More and more governments and MNOs are opting to expand their supplier ecosystem for greater flexibility and choice.
2) Open RAN Deployments Grow in Emerging Markets and Urban Environments
According to a TelecomTV survey, overall total cost of ownership is one of the most important considerations driving Open RAN in 2022 and beyond.
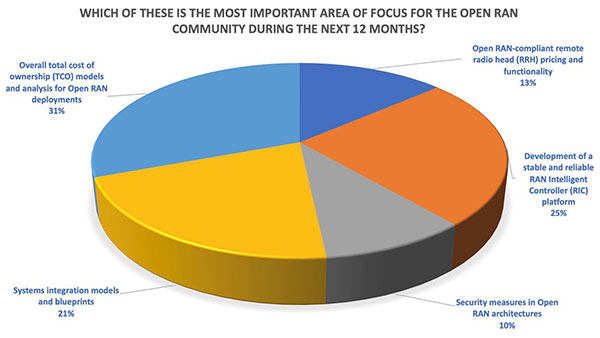
Cost-effective Open RAN is especially attractive in emerging markets where Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) is low and operators struggle to achieve positive Return on Investment (ROI). Open RAN in those regions can help unify different generations of technologies while allowing MNOs to avoid vendor lock-in, extend their existing network investments, and make any generation (G) – 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G cellular deployments unified, simplified, and automated. Using Open RAN as the architecture for deployments in emerging markets will enable wider coverage at affordable prices.
Meanwhile, consumers in urban environments demand higher speeds and faster throughput – and all for lower prices. As Open RAN evolves to utilize Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to automate networks, especially with features like Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP), it will be much easier to maintain and upgrade urban networks.
3) Number of Software Components Defined by the O-RAN Alliance Continue to Multiply
The original split of the wireless broadband network was driven by Release 15 of the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project). The O-RAN Alliance however refers to the key software components of the Open RAN network as the Radio Unit (O-RU) that performs lower layer signal and radio processing and RF functions, the Distributed Unit (O-DU) that performs packet scheduler and MAC layer functions, and the Central Unit (O-CU) that performs the high-level packet processing and cyphering type functions.
The separation of functionalities on southbound and northbound interfaces enables more efficient and cost-effective radio resource management for real-time and non-real-time functionalities.
In 2022 and beyond, we predict the O-RAN Alliance will continue to drive the next generation RAN to new levels of openness, efficiency, flexibility, and intelligence using reference designs, open interfaces, virtualization, open source and white box elements with more software driven components.
4) RIC Becomes More Mature with Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) – as the words indicate is the ‘intelligence’ behind the network – for Open RAN and will continue to evolve to enable eNB/gNB functionalities such as xApps on northbound interfaces. Applications such as mobility management, admission control, and interference management are available as apps on the controller, which enforce network policies via a southbound interface toward the radios. The RIC provides advanced control functionality, which delivers increased efficiency and better radio resource management. These control functionalities leverage analytics and data-driven approaches including advanced Machine Learning (ML)/Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools to improve resource management capabilities.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are imperative cloud-native automation tools needed to provide intelligent management and operations of the network, and the RIC will be key to enable these enhancements.
5) 5G Standalone Open RAN Networks Become the Ideal
Standalone core will be the deployment of choice for Open RAN networks in 2022 and beyond. The Open RAN movement helps to enable a broader and vibrant open ecosystem of complete solutions. Today, most 5G deployments are supported by existing 4G infrastructure where 5G radios are integrated into the existing 4G Evolved Packet Core (EPC). This is known as Non-Standalone (NSA). Non-Standalone will lock MNOs in with their existing vendors as the interfaces are not open and interoperable.
5G Standalone (SA) is the best option, utilizing Open RAN networks, as it is not dependent on 4G equipment and can deliver the capacity needed for 5G networks. With 5G SA, the network is simplified with 5G radios complemented by a next-generation open core network. 5G SA Open RAN networks are ideal for new applications as they provide ultra-reliable, lower-latency communications, allowing more people and devices to use mobile data at the same time, thus enabling true 5G connectivity.
6) Hyperscalers, the Edge and MNOs
The involvement of big public cloud providers, the “hyperscalers,” is an enormous game changer in favor of the Open RAN initiative. Hyperscalers – or cloud giants such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft – have been partnering with Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and will continue to do so in 2022 and beyond. For example, in April of 2021 Dish selected Amazon for their network Edge computing.
By both delivering the Open RAN management software and hosting the RAN network software together, public cloud providers could become very valuable partners to operators. Keep in mind, though, that real-time telecommunication transactions must be at the cell site where non-real time transactions can be in the cloud.
7) Open RAN Private Networks Revolutionize the Industry
Private Networks have always been a playground for new technologies, and Open RAN is no different. While Open RAN brings a variety of different options for operators, private networks can go a step further. Many countries are now setting some spectrum aside for private networks. Open RAN-based solutions are ready to take full advantage of this opportunity.
With many existing and new small cell and RRH players, there will be a variety of options available to small enterprises and large indoor/outdoor hybrid private networks. In addition, cloud-native solutions will allow the enterprises to take advantage of hyperscalers for the edge as well as for deploying the infrastructure software. This large ecosystem will create many choices for enterprises; thus Open RAN architecture is well suited for private networks.
Conclusion
As you can see from our predictions, we believe the future is open. Open RAN networks enable wireless best of breed RAN networks to be deployed faster and at lower costs, thus helping MNOs to deliver state-of-the-art broadband services across the globe.